Static vs. Media files in Django
June 18, 2019 • 4 min read
Django is a great Web framework for building Web applications in Python. It comes with a lot of batteries included that you’ll most likely need at some point in your project. Two of them took me a while to differentiate when I started: static and media files.
After helping some less experienced people, I feel like I’m not the only one running into this, so I’m hoping to clarify this in this post.
TL;DR
Static files are part of your application code, while media is for generated content by your application or users of your application.
Static files
Static files are managed by the staticfiles app which you need to install. It provides a couple of important blocks, the 3 most importants ones being:
- Storage classes
- Templates tags
collectstaticadmin command
These pieces work together to serve the sources in a more or less optimised way depending on your environment. This can be altered using the following settings:
STATIC_ROOTSTATIC_URLSTATICFILES_DIRSSTATICFILES_STORAGE
Static files are usually either part of your code, or part of your dependencies’ code. They can come from various places, each app may provide its own files. The Django admin ships with some javascript and CSS, for example.
In development, the setup is inefficient and optimised for convenience. It’s based on a view that looks into all the installed apps to find static files. In production, however this is done ahead of time via collectstatic, which copy all the static files into a single location, being another folder or somewhere on another machine, which could be in a different part of the world.
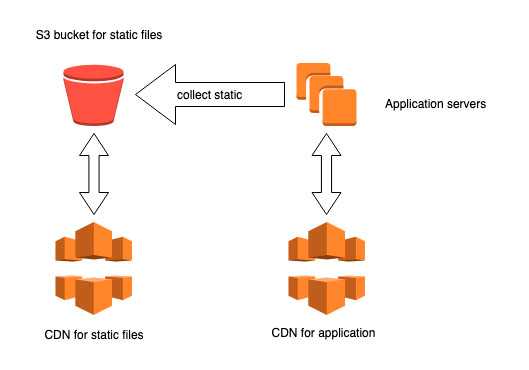
My go to solution used to be django-storages’s boto3 back-end for AWS S3 behind a CDN, which more or less gave this setup:
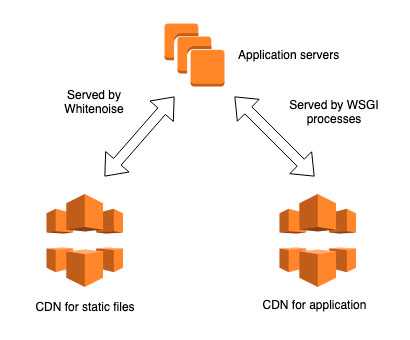
However, recently I’ve switched to Whitenoise, which leads to a simpler setup, and remove the need for a S3 bucket, all hosting comes from the Django app. The CDN should serve most of the traffic anyway:
I still use django-storages but only for media files, which brings us to the next section…
Media files
Media files are all files which are uploaded by users during the life of your Django project. This could be in the admin, the profile picture of the user or some more private documents like medical records, or legal copies. Basically, anything which is going into a FileField, ImageField or the likes is going into the media storage by default.
By default, files are stored on the local file system. The settings controlling this are:
MEDIA_ROOTMEDIA_URLDEFAULT_FILE_STORAGE
However, if you run your app on Heroku for instance, this default setup is not suitable for production, as the file system is ephemeral and is cleared each time the application is updated. This is where django-storages is still useful and needed.
If your app is hosting a mix of public media and private one, I recommend to define separate storage classes for each, you can tell in the field instantiation which storage class to use:
class User:
name = models.CharField()
# public file
profile_picture = models.ImageField(
storage=PublicStorage()
)
# private file
dbs_check_document = models.FileField(
storage=PrivateStorage()
)The django-storages library has several backends for various hosting providers with a lot of options to customise them, so I won’t go into the details of each, but here is an example of what it could look like for AWS:
from storages.backends.s3boto3 import S3Boto3Storage
class PublicStorage(S3Boto3Storage):
default_acl = 'public'
file_overwrite = False
bucket_name = 'my-public-bucket'
class PrivateStorage(S3Boto3Storage):
default_acl = 'private'
file_overwrite = False
bucket_name = 'my-private-bucket'Use different class locally and in production
There is one problem with the above approach, though: by defining your storage class on the model field, that means it would potentially be shared between you local environment and production, which is probably not what you want. To solve this, we can use a factory function to either use the local file system or a remote location, depending on a setting:
def get_storage(storage_type):
if settings.USE_REMOTE_STORAGE:
storage_class = {
'private': PrivateStorage,
'public': PublicStorage,
}[storage_type]
return storage_class()
return FileSystemStorage()Which would change your model definition to:
class User:
name = models.CharField()
# public file
profile_picture = models.ImageField(
storage=get_storage('public')
)
# private file
dbs_check_document = models.FileField(
storage=get_storage('private')
)In a real workd case, this helper should probably handle KeyError in the lookup and return the DEFAULT_FILE_STORAGE. You could also invent custom settings as you need.
Security concerns
If you decide to use django-storages for both Static and Media files, it’s important that you make the separation very clear, a user of your website shouldn’t be able to override one of your static assets by uploading a resource! I like to use a separate S3 Bucket for each type of storage. AWS has many options to customise the privacy of buckets and the objects their contain, and other providers have equivalent features.
Final note
While the Media storage might not be used by your application, the static files are a more essential, and any reasonable Django site will need it (at least for the admin).
I hope this post will help reduce the confusion I see frequently with beginners.